JWT Authentication
This section describes how to implement JWT Authentication.
The JWT Authentication allows integrating a Service Portal with CCX.
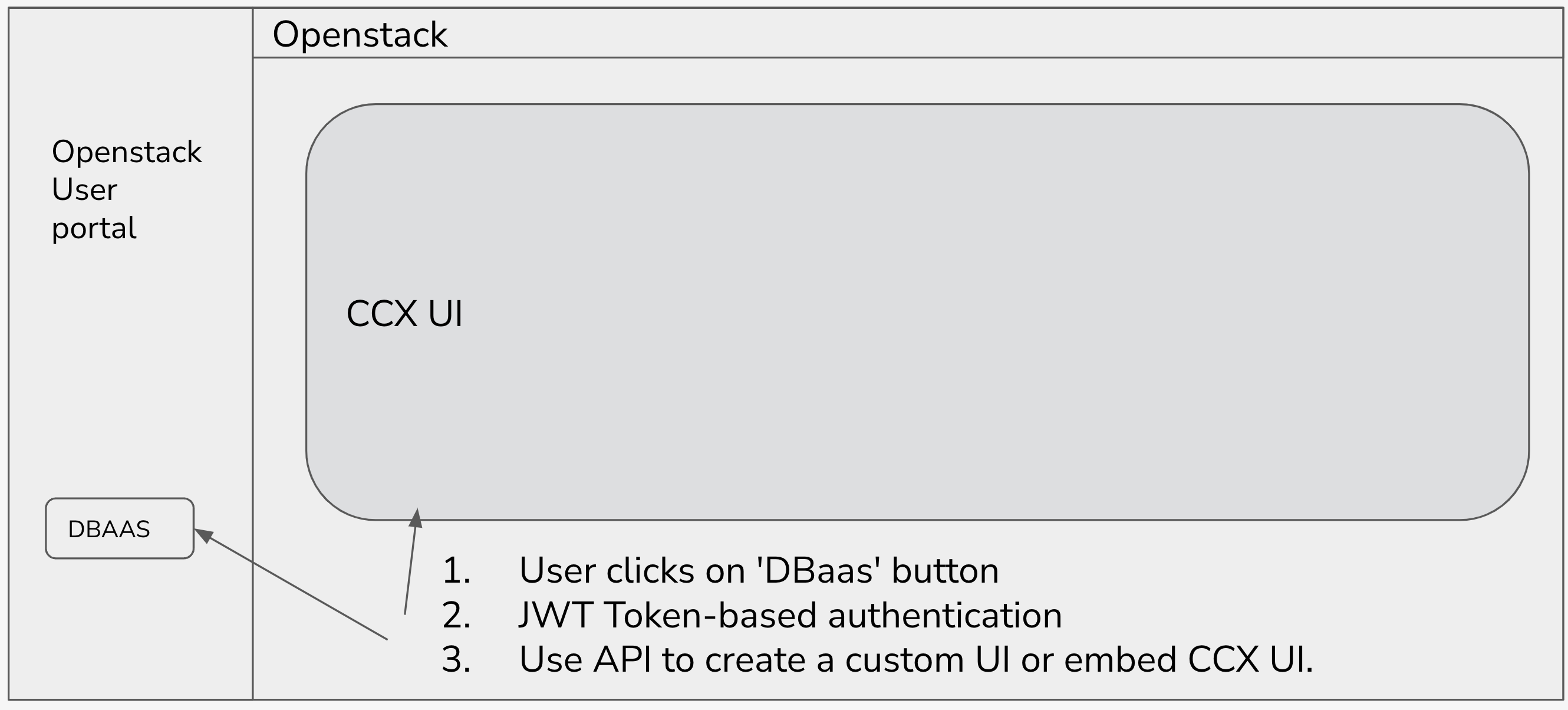
Users and Sessions Managed Using JWTs
The picture below shows the authentication flow:
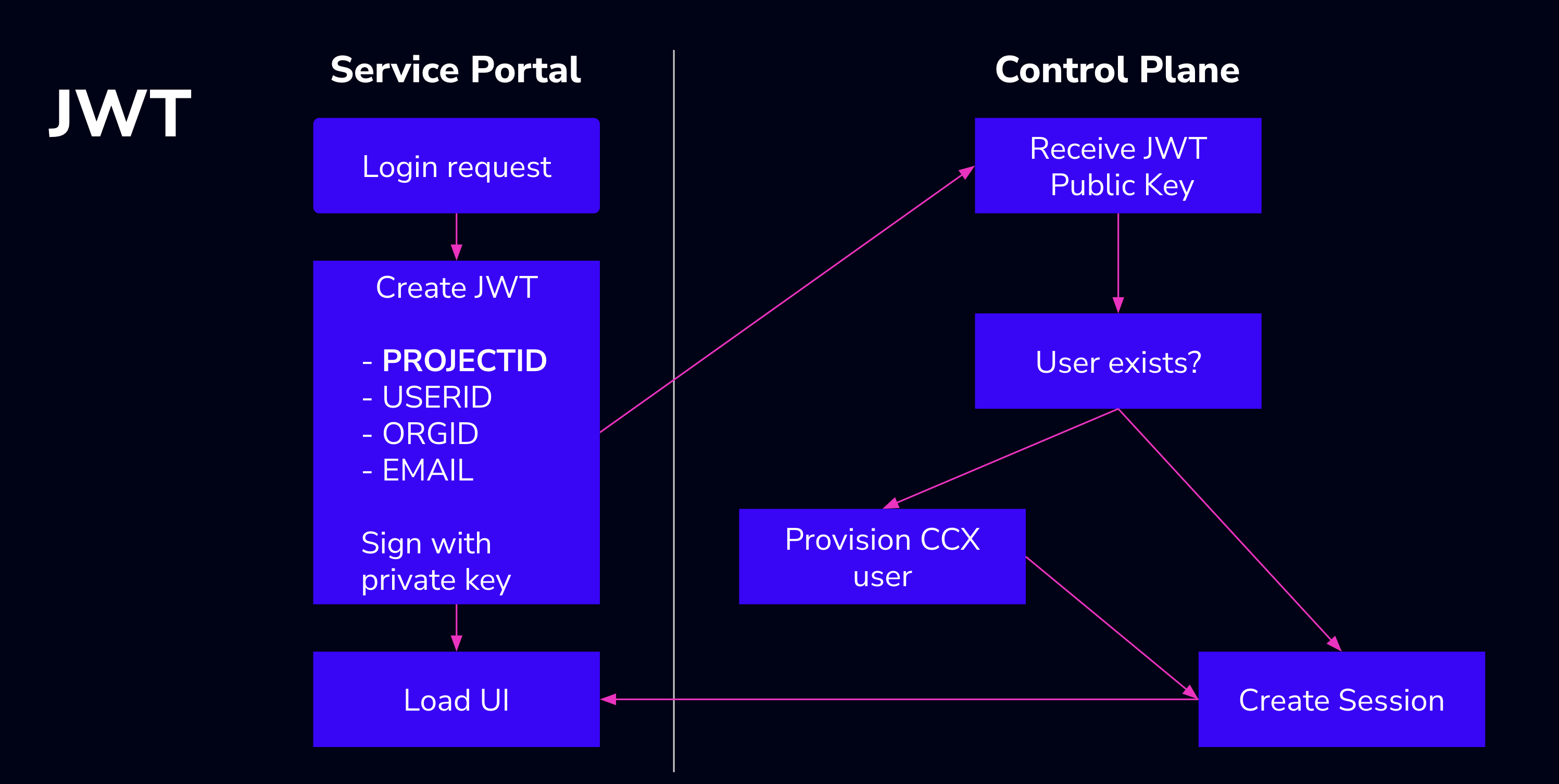
A JWT contains an associative array with claims about the user and session, and is signed by the issuer with a private key (RSA).
- The
jticlaim is a UUID identifying the session. - The
subclaim uniquely identifies the user. It can be a project id, an org id, a user id, an email address, or any other string that uniquely identifies your end-user.
CCX verifies JWTs using the corresponding public key (RSA), which is stored in the values file.
The private key is used by the intergrator/CSP to encrypt the JWT token (see examples). A key pair can be generated with:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -m PEM -f ccx.key
ssh-keygen -e -f ccx.key -m PEM > ccx.key.pub
Public key configuration in CCX Helm values:
You need to set the configuration parameters in ccx.services.auth in ccx values.yaml
env:
JWT_PUBLIC_KEY_ID: 'MYCLOUD'
JWT_PUBLIC_KEY_PEM: |-
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIICIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAg8AMIICCgKCAgEAxowkw7Zf2pXoehn2CkwQ
sHqbASdRp2DENgUEIGj+iqQPMDZor2CD1fVYpVZW+kcQkR9SgIvb+QiSgdHvWegs
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
JWT Environment Variables
| Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| JWT_PUBLIC_KEY_ID | The identifier of the provider, e.g., "MYCLOUD". |
| JWT_PUBLIC_KEY_PEM | The public key in PEM format (contents of ccx.key.pub). |
| JWT_PUBLIC_KEY_PKIX | Should be "1" if the key is in PKIX format (optional). |
JWT Endpoints
There are four endpoints for handling JWTs:
POST /api/auth/jwt-login
- Description: A new session is created. If the user doesn’t exist in the CCX database, a new user is created.
- Response: Returns
200 OKon success.
Request (JSON):
{
"issuer": "MYCLOUD",
"jwt": "JWT_TOKEN",
"first_name": "First Name (Optional)",
"last_name": "Last Name (Optional)"
}
Response (JSON):
{
"user": "User Info"
}
GET /api/auth/jwt-login
- Description: Creates a session for the provided user. The user must exist in the CCX database.
- Response: Returns
303 See otheron success. Redirects the user to the URL provided in theLOGIN_REDIRECT_URLenvironment variable inccx-auth-service.
Query Parameters:
issuer— the issuer of the JWT, e.g., "MYCLOUD".jwt— the JWT.
POST /api/auth/jwt-logout
- Description: Logs out the user. The associated session is deleted.
- Response: Returns
204 No contenton success.
Request (JSON):
{
"issuer": "MYCLOUD",
"jwt": "JWT_TOKEN"
}
POST /api/auth/jwt-check
- Description: Verifies the provided JWT. Returns its claims and the issuance and expiration dates.
- Response: Returns
200 OKon success.
Request (JSON):
{
"issuer": "MYCLOUD",
"jwt": "JWT_TOKEN"
}
Response (JSON):
{
"claims": "...",
"issued_at": "...",
"expires_at": "..."
}
Code sample
You can find a sample implementation here: ccx-jwt-sample on GitHub.
Examples of JWT Generation
Run the code by setting the params such as CCX_URL, MYCLOUD, USERID and Private Key
CCX_URL: E.g ccx.example.comMYCLOUD: The name of the cloud provider, examplemydbaasUSERID: Users with the the sameUSERIDwill see the same datastores. In Openstack e.g, there is a Project ID, if you want all users in a project to see the datastores, then you should set this to the Openstack Project Id.Private Key: The actual private key used to encrypt the token.
Go
This is an example and the code is provided as-is, no further support will be left on this code but feedback is welcome.
- Create a folder called jwt, and change to this folder
- Save the code in jwt.go
- go mod init jwt
- go mod tidy
- Change
CCX_URL,Private Keyetc - go run main.go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/x509"
"encoding/json"
"encoding/pem"
"errors"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
"fmt"
"github.com/golang-jwt/jwt"
"github.com/google/uuid"
)
const authUrlPrefix = "https://<CCX_URL>/api/auth"
var (
ErrBadPEMData = errors.New("malformed PEM data")
)
type jwtLoginRequest struct {
Issuer string `json:"issuer"`
Token string `json:"jwt"`
FirstName string `json:"first_name"`
LastName string `json:"last_name"`
}
func privateRSAKeyFromPEM(b []byte) (*rsa.PrivateKey, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(b)
if block == nil {
return nil, ErrBadPEMData
}
return x509.ParsePKCS1PrivateKey(block.Bytes)
}
func createJWT(issuer, subject string, exp time.Duration, key *rsa.PrivateKey) (string, error) {
now := time.Now()
claims := jwt.MapClaims{
"iss": issuer,
"sub": subject,
"jti": uuid.NewString(),
"iat": now.Unix(),
"exp": now.Add(exp).Unix(),
}
return jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodRS256, claims).SignedString(key)
}
func main() {
privKey, err := privateRSAKeyFromPEM(privateKey)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
token, err := createJWT("MYCLOUD", "USERID", 15*time.Minute, privKey)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
client := &http.Client{Timeout: 5 * time.Second}
in := &jwtLoginRequest{
Issuer: "MYCLOUD",
Token: token,
FirstName: "First_Name",
LastName: "Last_Name",
}
var buf bytes.Buffer
if err := json.NewEncoder(&buf).Encode(in); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodPost, authUrlPrefix+"/jwt-login", &buf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
log.Print("response status: ", resp.Status)
constructedURL := fmt.Sprintf("%s/jwt-login?jwt=%s&issuer=%s", authUrlPrefix, token, "MYCLOUD")
log.Printf("Constructed URL: %s", constructedURL) // Log the constructed URL
}
var (
privateKey = []byte(`-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
xxx
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----`)
)
JavaScript (Node.js)
This is an example and the code is provided as-is, no further support will be left on this code but feedback is welcome.
- Create a folder called jwt, and change to this folder
- Save the code as jwt.js
- npm install jsonwebtoken axios uuid
- Change
CCX_URL,Private Keyetc - node jwt.js
const fs = require('fs');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const axios = require('axios');
const { v4: uuidv4 } = require('uuid');
// --- Config ---
const authUrlPrefix = "https://<CCX_URL>/api/auth";
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync('./ccx.key', 'utf-8'); // path to your PEM file
// --- JWT Creation ---
function createJWT(issuer, subject, expMinutes, key) {
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
const payload = {
iss: issuer,
sub: subject,
jti: uuidv4(),
iat: now,
exp: now + expMinutes * 60,
};
return jwt.sign(payload, key, { algorithm: 'RS256' });
}
// --- Main Logic ---
async function main() {
try {
// Create the JWT
const token = createJWT("MYCLOUD", "USERID", 15, privateKey);
// Prepare the request body
const requestBody = {
issuer: "MYCLOUD",
jwt: token,
first_name: "First_Name",
last_name: "Last_Name"
};
// Send the POST request
const response = await axios.post(
`${authUrlPrefix}/jwt-login`,
requestBody,
{ timeout: 5000 } // 5 second timeout
);
console.log("response status:", response.status);
// Construct the login URL
const constructedURL = `${authUrlPrefix}/jwt-login?jwt=${encodeURIComponent(token)}&issuer=MYCLOUD`;
console.log("Constructed URL:", constructedURL);
} catch (err) {
console.error("Error:", err.message || err);
}
}
main();
Key Details
- Replace ./ccx.key with your actual key path, or inline the PEM if you want.
- Install required packages:
npm install jsonwebtoken axios uuid - The JWT is signed exactly as in Go example (RS256, same claims).
- The POST uses axios for simplicity (you can use native fetch in Node 18+, but axios is most similar to Go’s http.Client).
Typescript
This is an example and the code is provided as-is, no further support will be left on this code but feedback is welcome.
You will need these dependencies:
npm install jsonwebtoken axios uuid
npm install --save-dev @types/jsonwebtoken @types/node @types/uuid
Here is the code:
import * as fs from 'fs';
import * as jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
import axios from 'axios';
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
// ---- Types ----
interface JwtLoginRequest {
issuer: string;
jwt: string;
first_name: string;
last_name: string;
}
// ---- Config ----
const authUrlPrefix = "https://<CCX_URL>/api/auth";
// Load private key (PEM)
const privateKey: string = fs.readFileSync('./ccx.key', 'utf-8');
// ---- Functions ----
function createJWT(
issuer: string,
subject: string,
expMinutes: number,
key: string
): string {
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000); // seconds since epoch
const payload = {
iss: issuer,
sub: subject,
jti: uuidv4(),
iat: now,
exp: now + expMinutes * 60,
};
return jwt.sign(payload, key, { algorithm: 'RS256' });
}
async function main() {
try {
// Create JWT
const token = createJWT("MYCLOUD", "USERID", 15, privateKey);
// Prepare request payload
const reqBody: JwtLoginRequest = {
issuer: "MYCLOUD",
jwt: token,
first_name: "First_Name",
last_name: "Last_Name",
};
// Send POST request
const resp = await axios.post(
`${authUrlPrefix}/jwt-login`,
reqBody,
{ timeout: 5000 }
);
console.log("response status:", resp.status);
// Construct and print URL (as in Go)
const constructedURL = `${authUrlPrefix}/jwt-login?jwt=${encodeURIComponent(token)}&issuer=MYCLOUD`;
console.log("Constructed URL:", constructedURL);
} catch (err) {
if (axios.isAxiosError(err)) {
console.error("HTTP error:", err.message, err.response?.status);
} else {
console.error("Error:", err);
}
}
}
main();